Optimized Euler-Based Fermat Factorization Method Using Parallel Computing
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37256/cm.6620257692Keywords:
integer factorization, Fermat method, Euler theorem, number theory, parallel computing, cryptographyAbstract
The Euler-based Fermat Factorization (EFF) method is a technique used to factor a positive odd integer n into two prime factors p and q. The method is based on representing n as the difference between two squares and replacing the perfect square operation with modular multiplication. The computational time for the EFF method increases significantly with large values of n and d = |p−q| > 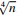 . This paper presents a new mathematical formula for computing the EFF method in a parallel shared-memory model. Then, it proposes a new parallel algorithm to speed up the computation of factorization when n is large and d exceeds
. This paper presents a new mathematical formula for computing the EFF method in a parallel shared-memory model. Then, it proposes a new parallel algorithm to speed up the computation of factorization when n is large and d exceeds 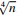 . Experiments were conducted on a multicore system to evaluate the performance of the proposed method across various parameters, including the size of n, the difference d, and the number of threads in the parallel system. The results show that the proposed parallel EFF algorithm achieves performance enhancements of 77.3% compared to the original EFF algorithm and 47.7% relative to the best-known parallel algorithm. Furthermore, the parallel EFF algorithm demonstrates superior scalability compared to the best-known parallel algorithm.
. Experiments were conducted on a multicore system to evaluate the performance of the proposed method across various parameters, including the size of n, the difference d, and the number of threads in the parallel system. The results show that the proposed parallel EFF algorithm achieves performance enhancements of 77.3% compared to the original EFF algorithm and 47.7% relative to the best-known parallel algorithm. Furthermore, the parallel EFF algorithm demonstrates superior scalability compared to the best-known parallel algorithm.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Hazem M. Bahig, et al.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

