Global Solvability of the Generalized Boussinesq System with Linear or Nonlinear Buoyancy Force
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37256/cm.6520257734Keywords:
global solvability, Boussinesq system, fractional Laplacian, linear or nonlinear buoyancy forceAbstract
This paper is devoted to the global solvability of the Boussinesq system with fractional Laplacian (−∆)α in 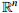 for n ≥ 3, where the buoyancy force has the form |θ|m−1θen with m ≥ 1. By establishing estimates for the difference |θ1|m−1θ1 − |θ2|m−1θ2 in Besov spaces and employing the maximal regularity property of (−∆)α in Lorentz spaces, we prove the following results: under some reasonable assumptions on the exponents α, m, p, r and ρ, if the small initial data of velocity and temperature (or salinity) fall in
for n ≥ 3, where the buoyancy force has the form |θ|m−1θen with m ≥ 1. By establishing estimates for the difference |θ1|m−1θ1 − |θ2|m−1θ2 in Besov spaces and employing the maximal regularity property of (−∆)α in Lorentz spaces, we prove the following results: under some reasonable assumptions on the exponents α, m, p, r and ρ, if the small initial data of velocity and temperature (or salinity) fall in 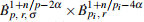 (where p1 = p for 1 < p < n, and p2 = p/2 for n ≤ p < 2n) when m = 1, and in
(where p1 = p for 1 < p < n, and p2 = p/2 for n ≤ p < 2n) when m = 1, and in 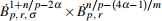 when m > 1, then the generalized Boussinesq system admits a unique global strong solution (u, θ) in
when m > 1, then the generalized Boussinesq system admits a unique global strong solution (u, θ) in 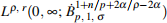 ×
× 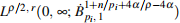 (with i = 1, 2 cor-responding to the definition of p1, p2) for m = 1 and in
(with i = 1, 2 cor-responding to the definition of p1, p2) for m = 1 and in 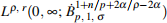 ×
× 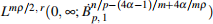 for m > 1, respectively.
for m > 1, respectively.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Qinghua Zhang, et al.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

