Decay of Mass for a Semilinear Heat Equation on Heisenberg Group
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37256/cm.6520258109Keywords:
large time behavior of solutions, semilinear parabolic equations, Heisenberg group, mass, critical exponentAbstract
In this paper, we are concerned with the Cauchy problem for a reaction-diffusion equation with time-dependent absorption, posed on the Heisenberg group 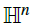 , driven by the sub-Laplacian and supplemented with non-negative integrable initial data. The equation includes a nonlinear absorption term of the form
, driven by the sub-Laplacian and supplemented with non-negative integrable initial data. The equation includes a nonlinear absorption term of the form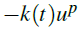 , where
, where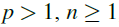 , and
, and 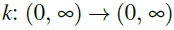 is a locally integrable function. The main focus is on how the interplay between nonlinear absorption and diffusion determines the long-time behavior of solutions. We show that the nonlinear term determines the large-time asymptotic behavior when
is a locally integrable function. The main focus is on how the interplay between nonlinear absorption and diffusion determines the long-time behavior of solutions. We show that the nonlinear term determines the large-time asymptotic behavior when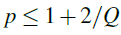 , while the classical/anomalous diffusion effects win if
, while the classical/anomalous diffusion effects win if 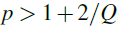 , where
, where 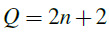 is the homogeneous dimension of Hn. The novelty of this work lies in extending the asymptotic analysis of nonlinear parabolic equations with time-dependent absorption from the classical Euclidean setting to the sub-Riemannian geometry of the Heisenberg group. To our knowledge, this is the first classification of large-time behavior for such equations in this setting. Our analysis relies on different mathematical techniques tailored to the nature of the results. The proof of the main decay result uses
is the homogeneous dimension of Hn. The novelty of this work lies in extending the asymptotic analysis of nonlinear parabolic equations with time-dependent absorption from the classical Euclidean setting to the sub-Riemannian geometry of the Heisenberg group. To our knowledge, this is the first classification of large-time behavior for such equations in this setting. Our analysis relies on different mathematical techniques tailored to the nature of the results. The proof of the main decay result uses 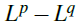 estimates for the solutions along with a comparison principle, while for the sub-critical case, we apply the method of nonlinear capacity estimates, also known as the rescaled test function method, which is particularly effective in capturing subtle asymptotic behavior.
estimates for the solutions along with a comparison principle, while for the sub-critical case, we apply the method of nonlinear capacity estimates, also known as the rescaled test function method, which is particularly effective in capturing subtle asymptotic behavior.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ahmad Fino

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

