Modulation Instability and Novel Exact Soliton Solutions of the Nonlocal Kundu-Eckhaus Equation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37256/cm.6620258233Keywords:
nonlinear optics, nonlinear Kundu-Eckhaus equation, analytical method, Modulation Instability (MI)Abstract
Diverse fields of modern science, including mathematical modeling and physics, plasma physics, atmospheric sciences, marine sciences, hydrodynamics, nonlinear mechanics, and other complex nonlinear physical phenomena, are expressed through Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations (NLPDEs). Exact solutions play an important role in understanding the behavior of solitary wave solutions and the dynamical properties of significant outcomes for higher-dimensional NLPDEs. As an integrable extension of the nonlinear Schrödinger equation, the nonlocal Kundu-Eckhaus model comprehends higher-order nonlinearities and nonlocal effects. The stability properties of dark, bright, periodic multiple, and singular soliton solutions to the nonlocal Kundu-Eckhaus (KE) equation within the Parity-Time (PT) symmetry model are studied here, whereas past studies have neglected the effects of nonlocal interactions and PT symmetry. 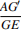 is a well-established method, particularly for depicting wave dynamics in nonlinear optical and quantum systems. We attain exact traveling wave solutions evolved in hyperbolic and trigonometric forms, representing several classes of solitons by applying this method. The findings elucidate that the obtained soliton solutions are stable under small perturbations, highlighting their robustness and the persistence of localized waveforms in nonlocal circumstances. We plotted 3D, 2D, and contour graphs for simulating our findings using MATLAB. This research sheds light on the mysterious understanding of nonlocal nonlinear wave behaviors and offers analytical methodologies for future scrutiny in fields such as optical physics and complex nonlinear systems.
is a well-established method, particularly for depicting wave dynamics in nonlinear optical and quantum systems. We attain exact traveling wave solutions evolved in hyperbolic and trigonometric forms, representing several classes of solitons by applying this method. The findings elucidate that the obtained soliton solutions are stable under small perturbations, highlighting their robustness and the persistence of localized waveforms in nonlocal circumstances. We plotted 3D, 2D, and contour graphs for simulating our findings using MATLAB. This research sheds light on the mysterious understanding of nonlocal nonlinear wave behaviors and offers analytical methodologies for future scrutiny in fields such as optical physics and complex nonlinear systems.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Shams Forruque Ahmed, et al.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

