Dynamical Systems Perspective on a Stochastic SIR Model with Multiplicative Noise
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37256/cm.7120269024Keywords:
Susceptible-Infected-Recovered (SIR) model, basic reproduction number, stochastic differential equations, numerical simulationsAbstract
We analyze a stochastic Susceptible-Infected-Recovered (SIR) epidemic model incorporating multiplicative environmental noise. Starting from positive initial conditions, we establish global existence, uniqueness, and strict positivity of strong solutions. Using the Lyapunov function method, we derive time-average fluctuation bounds around the disease-free equilibrium when R0 < 1 and around the endemic equilibrium when R0 > 1. In the stochastic setting, a noise-adjusted reproduction number is obtained via a logarithmic transformation of the infected population, 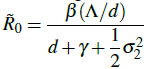 , which explicitly reduces to the deterministic basic reproduction number
, which explicitly reduces to the deterministic basic reproduction number 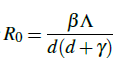 when σ2 =0, ensuring consistency with Section 6. Under this threshold, the infection becomes extinct almost surely if
when σ2 =0, ensuring consistency with Section 6. Under this threshold, the infection becomes extinct almost surely if 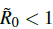 , while additional analytical results establish stochastic persistence when
, while additional analytical results establish stochastic persistence when 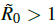 . Numerical simulations employing the Milstein scheme confirm these analytical findings: increasing the noise intensity σ2 amplifies fluctuations and can shift long-run behavior from persistence to extinction. Extensions to include additional removal terms h(I) are briefly discussed.
. Numerical simulations employing the Milstein scheme confirm these analytical findings: increasing the noise intensity σ2 amplifies fluctuations and can shift long-run behavior from persistence to extinction. Extensions to include additional removal terms h(I) are briefly discussed.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Shah Hussain, Mohammed Alghazi, Najla A. Mohammed, Ilyas Khan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

