Enhanced Biodiesel Production from Waste Cooking Oil Using Potash-Enriched Natural Base Catalyst
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37256/sce.5220244778Keywords:
waste cooking oil, heterogeneous catalyst, sugar apple peel ash, biodieselAbstract
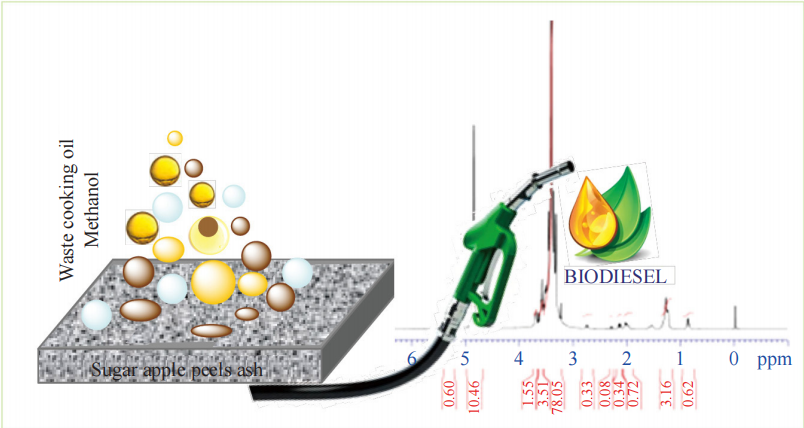
The transesterification reaction of waste cooking oil with methanol using a sugar apple peel ash catalyst has been reported. Under optimized conditions, the reaction of the oil with methanol in a molar ratio of 1 : 10, in the presence of 2 g of catalyst at 60 °C, resulted in a 94.5% yield of biodiesel within 120 min. The heterogeneous catalyst was developed via a straightforward calcination process using waste peels from the fruit processing industry of sugar apples. Characterization of the catalyst by FTIR, EDS, SEM, XRD, N2 sorption, and XRF analysis revealed a high concentration of potassium species, which are likely responsible for enhancing the efficiency of the transesterification reaction. This approach offers cost competitiveness, catalyst reusability, operational simplicity, and high biodiesel yields. This study underscores the potential of utilizing waste materials for sustainable biodiesel production, contributing to environmental preservation and economic viability.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 U. P. Patil, S. U. Patil

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

