Computational Studies of Biodegradation of Polyester-Polyurethanes by Protease Enzyme
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37256/sce.5220245188Keywords:
Polyurethane, HDI, IPDI, Bio degradations, DFT and MD simulationsAbstract
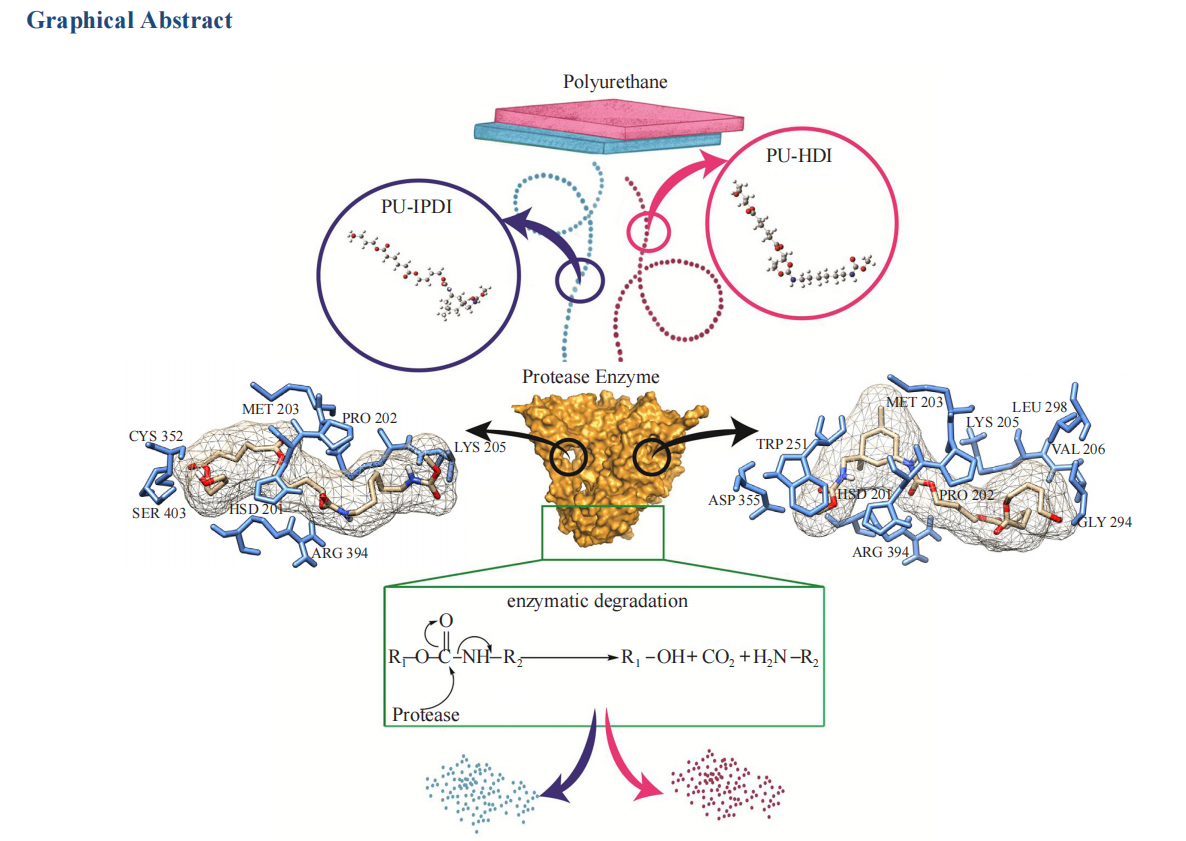
Polyurethane (PU) is a widely used synthetic polymer with significant environmental concerns. Recent research into PU biodegradation, especially via protease enzymes, shows potential, yet the degradation mechanisms are not fully understood. This study investigates the binding interactions between protease and two PU variants: polybutylene adipate with 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate (PU-HDI) and 5-isocyanato-1-(isocyanatomethyl)-1,3,3-trimethylcyclohexane (PU-IPDI). Using 150-ns molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, a shift towards more stable conformations was observed, with residues in the most favored regions increasing from 63.2% to 86.3% in the Ramachandran plot. Density Functional Theory (DFT)-optimized PU ligands were docked into the enzyme's binding pocket and validated by tunnel analysis. Docking studies revealed distinct stabilizing interactions for each PU variant: PU-HDI's urethane linkage formed a strong hydrogen bond with HSD201, while PU-IPDI's urethane linkage bonded with ARG394 and PRO202. MD simulations confirmed the stability of these complexes, emphasizing persistent hydrogen bonds. Analysis of urethane bond lengths identified potential enzymatic degradation initiation sites. The binding of PU monomers reduced the protease enzyme's flexibility, indicating a significant structural impact. The MM/PBSA method confirmed substantial interactions between PU and the protease, supporting the study's findings. This research offers vital insights into aliphatic PU and protease interactions, advancing the development of biodegradable materials.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Baggya Karunarathna, G. M. S. T. Gajasinghe, V. T. Hewage, K. K. Govender, M. B. A. Prashantha, J. D. Wanniarachchi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

