Environmentally Benign Green Approach for the Synthesis of IONPs Using Vicia Faba Fruit Extract and Their Antioxidant Activities
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37256/sce.6120255306Keywords:
green synthesis, iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs), vicia faba fruit extract, bioreducing agents, antioxidant activity, DPPH radicals, nanoparticles (NPs)Abstract
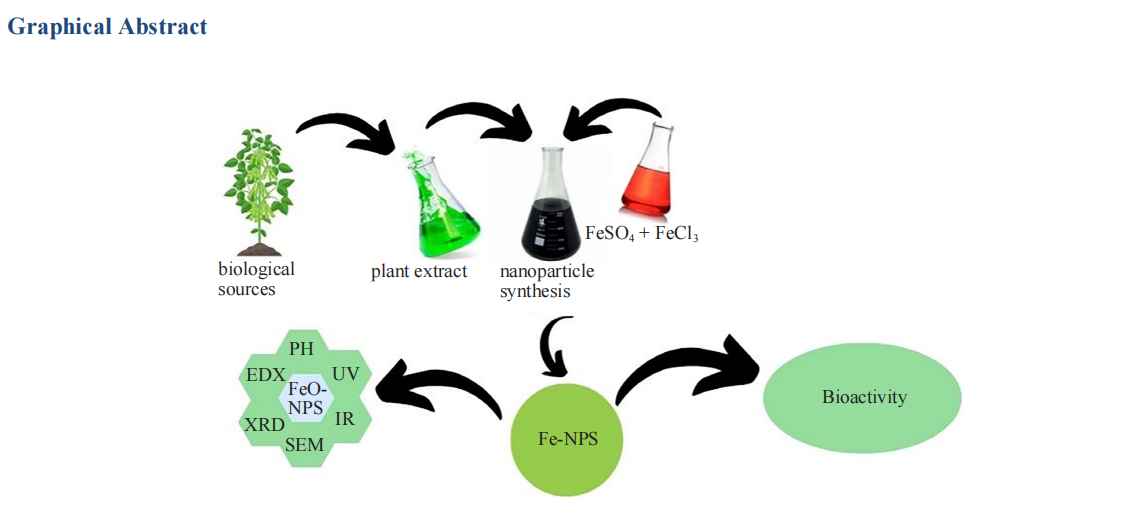
Iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized from plant materials have garnered considerable attention due to their environmentally friendly nature and wide-ranging applications in various fields. These NPs possess unique attributes, including biocompatibility, low toxicity, catalytic capabilities, and intricate reaction mechanisms, making them highly desirable for diverse biomedical uses. This study presents an innovative green synthesis approach utilizing the fruit extract of Vicia faba (V. faba). The synthesized NPs underwent comprehensive characterization using advanced techniques such as Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), UV-visible spectrophotometry, X-ray diffractometry (XRD), and scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX). Notably, the V. faba fruit extract served as an effective reducing agent, facilitating the synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) with well-defined structural and chemical properties. The size of iron oxide nanoparticles ranges from 299.3 to 527.4 nm. Furthermore, the synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles were evaluated for their antioxidant activity, revealing promising results against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and 2,2'-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radicals. These findings highlight the significance of V. faba fruit extract in producing IONPs endowed with valuable bioactive properties, offering considerable potential for applications in biomedicine and beyond.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Rucika Prakash, Ruchi Bharti, Ajay Thakur, Monika Verma, Renu Sharma

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

