Integrated Advanced Ozonation Technologies for Enhanced Total Organic Carbon Removal from Secondary Treated Municipal Wastewater: Systematic Optimization and Environmental Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37256/sce.6120255891Keywords:
adsorption, peroxone treatment, ozonation, total organic carbon removal, wastewater treatmentAbstract
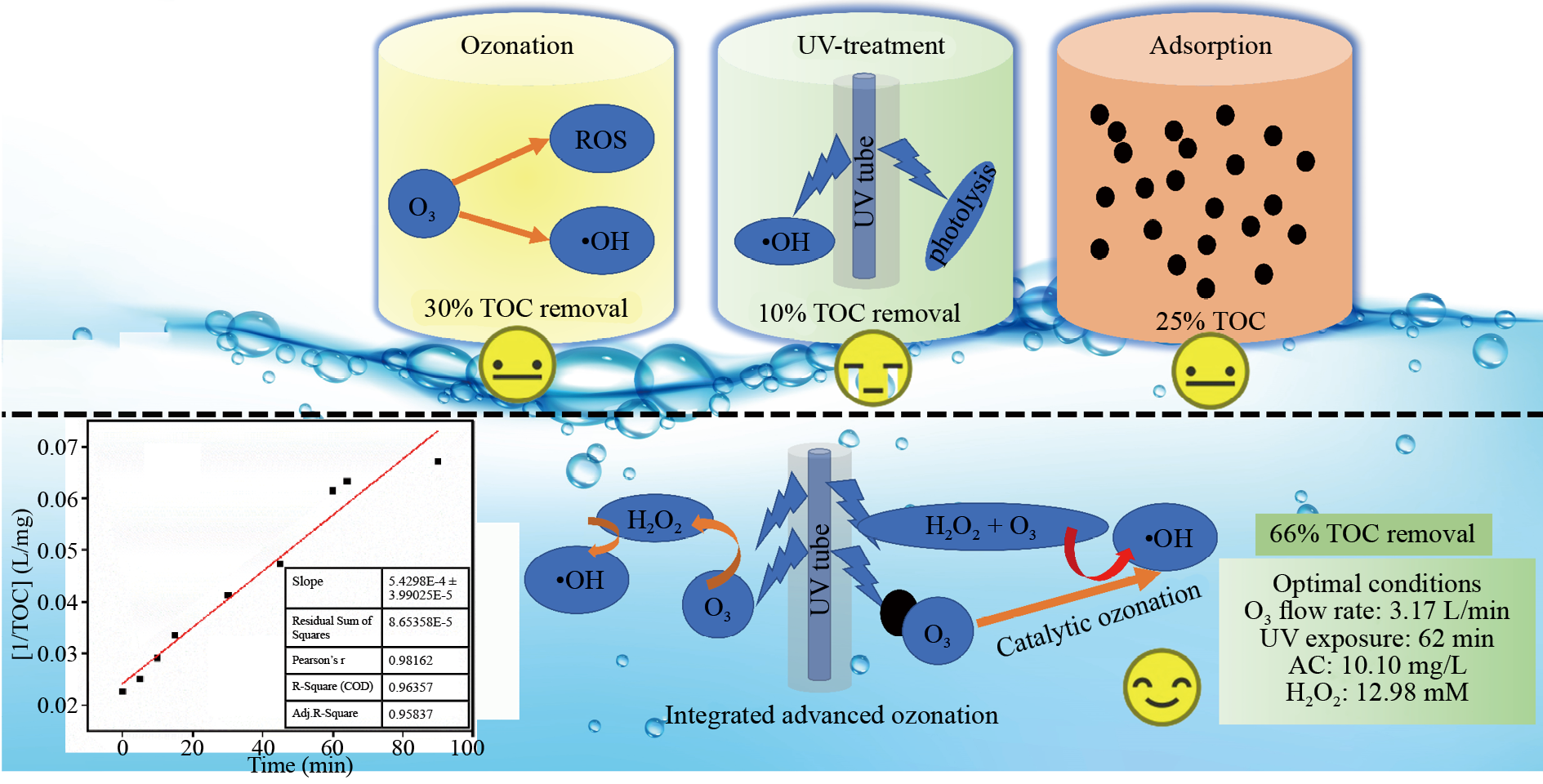
Municipal wastewater, characterized by a complex matrix of organic contaminants, poses significant environmental challenges due to residual total organic carbon (TOC), a critical marker of persistent organic pollutants, even after secondary treatment. To address this issue, the investigation evaluates the efficiency of integrated advanced ozonation technologies combining ozone (O3), ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and activatedcarbon (AC) for TOC removal from secondary-treated effluent. A predictive model optimized the process parameters, achieving a maximum TOC removal efficiency of 65.95% at an O3 flow rate of 3.17 L/min, H2O2 dosage of 12.98 mM, UV exposure duration of 62.04 min, and AC dosage of 10.10 mg/L. In contrast, the lowest TOC removal of 39.55% ± 2.15% occurred under sub-optimal conditions, with an O3 flow rate of 3 L/min, H2O2 dosage of 10 mM, UV exposure for 20 min, and 1 mg/L of AC. The economic and environmental analyses revealed the integrated process to be more cost-effective and sustainable compared to conventional single-step treatments. These findings highlight the potential of integrated advanced ozonation technologies for effective TOC removal, providing a pathway for enhanced wastewater treatment practices and improved environmental sustainability.
Graphical Abstract
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Akash Tripathi, Rahul Gorai, M. M. Ghangrekar, Brajesh Kumar Dubey

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

